ISRO Upcoming Missions 2025: A Deep Dive Into India’s Space Ambitions
Isro upcoming missions 2025 With the successful launches of Chandrayaan-3 and Aditya-L1 in 2023, and a series of scientific and commercial missions in 2024, ISRO has set its sights even higher. The year 2025 promises a major leap forward in India’s space journey, with several exciting and strategically significant ISRO upcoming missions planned across diverse areas like space exploration, satellite technology, space science, and human spaceflight.
In this comprehensive article, we will explore all the major ISRO missions in 2025, their objectives, timelines, technological significance, and how they align with India’s broader ambitions in space.
1. Gaganyaan Human Spaceflight Mission | isro upcoming missions 2025
Overview
The mission aims to send three Indian astronauts (Gagannauts) to low Earth orbit (~400 km) for a mission duration of up to 3 days.
Mission Objectives
- Demonstrate India’s human spaceflight capability.
- Test life support, safety systems, reentry technologies, and crew module performance.
Timeline and Testing | isro upcoming missions 2025
As of now, ISRO has conducted various precursor missions including:
- Test Vehicle Abort Missions (TV-D1 & D2) to verify crew escape systems.
- Uncrewed Gaganyaan flights to test the spacecraft systems in real flight conditions.
The crewed mission is expected by late 2025, depending on the success of these tests.
International Collaboration
ISRO is collaborating with Roscosmos (Russia) for astronaut training and with NASA and ESA for space medicine and life support technologies.
2. Chandrayaan-4: Lunar Sample Return Mission | isro upcoming missions 2025
Following the success of Chandrayaan-3, ISRO is preparing Chandrayaan-4, a lunar sample return mission—a first for India. This ambitious project aims to land on the Moon, collect regolith samples, and return them to Earth.
Importance
- Establishes advanced lunar exploration capability.
- Enables study of Moon’s mineralogy and age.
- Positions India alongside NASA and CNSA (China) in sample-return technologies.
Technical Highlights
- Dual-launch strategy with orbiter and lander.
- Robotic arm or drill mechanism for sample collection.
- Complex Earth reentry trajectory.
The mission is tentatively scheduled for late 2025 or early 2026, depending on development timelines.
3. Shukrayaan-1: India’s First Venus Mission | isro upcoming missions 2025
Why Venus?
Venus is often considered Earth’s twin due to its size and composition, but its extreme greenhouse climate makes it a compelling subject for study.
Scientific Goals
- Study Venus’s dense atmosphere and cloud layers.
- Analyze surface geology using radar mapping.
- Investigate signs of active volcanism or seismic activity.
Payloads and Instruments
- Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) for surface mapping.
- UV spectrometer, airglow camera, and ion analyzers.
Though originally targeted for 2024, Shukrayaan-1 is now expected in mid-to-late 2025, depending on launch window availability and readiness of payloads.
4. NISAR Mission (NASA-ISRO SAR) | isro upcoming missions 2025
A Global Collaboration

NISAR (NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar) is a joint Earth observation mission between ISRO and NASA. It is designed to monitor climate change, ice mass changes, agricultural patterns, and natural disasters.
Mission Highlights
- Satellite weighs over 2800 kg, to be launched by GSLV Mk II or Mk III.
- Data to be used for over 10 years of Earth science research.
Expected to launch by early 2025, this mission marks one of the largest collaborations in Earth sciences between India and the US.
5. Aditya-L2 and Solar Research Expansion
While an official Aditya-L2 has not yet been named, the follow-up solar mission is expected to be proposed in late 2025 for launch in 2026 or 2027.
Focus areas include:
- Helioseismology.
- CME (Coronal Mass Ejection) tracking.
- High-resolution spectroscopy.
6. Commercial Satellite Launches and Small Satellite isro upcoming missions 2025
PSLV-C and SSLV Series
ISRO is set to conduct multiple commercial launches using the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) and Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) in 2025. These launches will serve:
- Domestic payloads (telecom, agriculture, remote sensing).
- International commercial clients under Antrix and NSIL.
With the growing demand from space startups, ISRO is working with private players like Skyroot, Agnikul Cosmos, and Bellatrix.
ISRO’s Private Sector Partnerships | isro upcoming missions 2025
India’s space economy is expected to grow to $13 billion by 2025, and ISRO’s collaboration with the private sector through IN-SPACe will play a vital role in democratizing access to space.
7. Mars Orbiter Mission-2 (Mangalyaan-2)
Status and Prospects

- An orbiter with more advanced instruments.
- Potential lander/rover configuration.
- Participation of international science payloads.
The goal is to continue India’s planetary science efforts and study seasonal and surface phenomena on Mars.
8. Space Station Plans and R&D Initiatives | isro upcoming missions 2025
While India’s own space station is not expected before 2035, ISRO will begin preliminary R&D activities in 2025. These include:
- Development of autonomous docking systems.
- Long-duration habitat modules.
- Life support and closed-loop ecosystems.
India may also join international space station experiments through collaboration with NASA or Roscosmos.
9. Satellite Constellation for Navigation and Communication
Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC) Expansion | isro upcoming missions 2025
In 2025, ISRO will continue expanding the NavIC (India’s GPS-like system) with new-generation satellites providing:
- L1 band signal support for smartphones.
- Higher accuracy for logistics, military, and disaster management.
GSAT and COMSAT Missions
GSAT satellites for communication, especially in Ku-band and Ka-band, will be launched in 2025 to improve:
- Rural broadband.
- Disaster response.
- Secure communications.
10. ISRO’s Scientific and Academic Missions | isro upcoming missions 2025
ISRO will continue supporting academic satellite missions in 2025 in partnership with institutions like:
- Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology (IIST).
- IITs and private universities.
These micro- and nano-satellites serve purposes like:
- Atmospheric research.
- Student training.
- Low-cost innovation testbeds.
A Snapshot of ISRO’s 2025 Launch Calendar (Tentative) | isro upcoming missions 2025
| Mission Name | Type | Launch Vehicle | Estimated Launch |
| Gaganyaan | Human Spaceflight | GSLV Mk III | Q4 2025 |
| Chandrayaan-4 | Lunar Sample Return | GSLV Mk III | Q4 2025 / Q1 2026 |
| Shukrayaan-1 | Planetary Science (Venus) | GSLV Mk II | Q3/Q4 2025 |
| NISAR | Earth Observation | GSLV Mk II | Q1 2025 |
| NavIC Satellites | Navigation | PSLV | Throughout 2025 |
| GSAT Series | Communication | GSLV Mk II | Throughout 2025 |
| SSLV Commercials | Small Satellite Launches | SSLV | Ongoing |
Challenges Ahead
Despite its success, ISRO faces several challenges:
- Budget constraints compared to global peers.
- Talent retention amid growing private space sector.
- Coordination with startups while maintaining national security standards.
However, 2025 stands as a pivotal year to overcome these hurdles and establish India as a leading global space player.
What is the Mission of ISRO in 2025? | isro upcoming missions 2025
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), known for its cost-effective and highly efficient space missions, is poised for a transformative year in 2025. With a blend of ambitious scientific objectives, technological advancements, and international collaborations, ISRO’s mission for 2025 reflects India’s growing presence in the global space community.
From lunar exploration to space station development and satellite launches, ISRO’s roadmap for 2025 is dynamic and impactful. In this detailed article, we explore ISRO’s key goals, major projects, isro upcoming missions 2025 launches, and its broader mission in 2025.
ISRO’s Broad Mission Objectives in 2025 | isro upcoming missions 2025
Before diving into individual projects, it is important to understand ISRO’s overarching mission in 2025. The core objectives include:
- Pushing boundaries in space science through interplanetary and planetary missions.
- Promoting private space industry participation through the Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center (IN-SPACe).
- Focusing on sustainability and climate monitoring through satellite data and international collaboration.
Let’s now break down the specific missions and initiatives expected in 2025.
1. Gaganyaan Mission: India’s First Human Spaceflight | isro upcoming missions 2025
🚀 Mission Overview
Gaganyaan is India’s first crewed mission and a major part of ISRO’s 2025 agenda. After years of testing, 2025 is expected to be the year when Indian astronauts are launched into low-Earth orbit aboard an indigenous spacecraft.
🧑🚀 Key Features:
- Crew Module: Designed to carry 2–3 astronauts.
- Launch Vehicle: Modified version of the GSLV Mk III (renamed LVM-3).
- Duration: 3–7 days in orbit.
- Altitude: Around 400 km from Earth’s surface.
- Training: Astronauts are receiving training in India and Russia.
🌐 Significance:
It will also open pathways to future space station modules and Moon missions.
2. Chandrayaan-4: Lunar Sample Return Mission | isro upcoming missions 2025
After the success of Chandrayaan-3 in 2023, which successfully landed near the lunar south pole, ISRO has been planning a follow-up mission: Chandrayaan-4.
🧪 Mission Goals: (isro upcoming missions 2025)
- Further study lunar geology, especially in permanently shadowed regions.
🤝 Possible Collaborations:
ISRO may work with JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) or ESA (European Space Agency) for technology and support in re-entry modules.
3. Aditya-L1 Mission (Ongoing Observations)
While launched in 2023, the Aditya-L1 solar mission is expected to continue delivering data through 2025.
☀️ Mission Highlights:
- Crucial for understanding space weather and solar events that impact Earth.
📡 Importance in 2025 (isro upcoming missions 2025):
Solar maximum is expected around 2025, making Aditya-L1’s data especially valuable for studying solar flares and CMEs (Coronal Mass Ejections).
4. Shukrayaan-1 (Venus Mission) – Under Development | isro upcoming missions 2025
Although launch timelines are flexible, Shukrayaan-1, ISRO’s proposed mission to Venus, is a key project in late-stage planning by 2025.
🌌 Mission Objectives:
- Study Venus’s dense atmosphere, surface temperature, and volcanic activity.
- Understand why Venus evolved so differently from Earth.
If not launched in 2025, this mission will likely reach final design and testing stages during the year.
5. Next-Generation Launch Vehicles (NGLV)
ISRO aims to modernize its launch fleet with reusable and heavier-payload rockets.
🚀 Key Features of NGLV:
- Semi-cryogenic propulsion.
- Designed for reusability and commercial satellite launches.
By 2025, ISRO is expected to complete major milestones in NGLV development, including full-scale testing and suborbital flights.
6. Indian Space Station (Bharatiya Antariksha Station)
🧱 2025 Objectives:
- Design and testing of modular components.
- Space habitation module R&D.
- Environmental control and life support system trials.
India’s vision is to place a small, modular space station in orbit, with potential to host astronauts and experiments independently.
7. Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) Commercialization | isro upcoming missions 2025
After successful launches in 2022–2024, SSLV is set for mass production and commercial use in 2025.
📦 Key Applications:
- Deploying small satellites for startups and foreign clients.
- On-demand launch capability with rapid turnaround.
SSLV helps ISRO tap into the growing market of small satellite constellations for Earth imaging and IoT.
8. Earth Observation and Weather Satellites
🛰️ Key Missions:
- RISAT (Radar Imaging Satellites) for defense and disaster management.
- Oceansat and INSAT series for ocean monitoring, agriculture, and meteorology.
In 2025, these satellites will enhance India’s precision farming, water management, and disaster preparedness capabilities.
9. ISRO’s International Collaborations in 2025 | isro upcoming missions 2025
ISRO continues to strengthen ties with global space agencies. Key collaborations include:
- NASA-ISRO SAR (NISAR) mission to map Earth’s surface deformation.
- Bilateral projects with France, Russia, UAE, and Japan.
- Space diplomacy through satellite launches for developing nations under the “Satellite for South Asia” initiative.
10. Private Sector & Startups: The IN-SPACe Initiative
IN-SPACe, the regulatory body for private space participation, is expected to scale up in 2025.
🔧 What to Expect:
- More private satellite launches.
- Testing of private launch vehicles.
- Use of ISRO facilities by startups like Skyroot, Agnikul, and Bellatrix.
This supports India’s goal of isro upcoming (missions 2025) a global hub for affordable space services.
Challenges Ahead for ISRO in 2025 | isro upcoming missions 2025
While 2025 promises big achievements, ISRO faces several challenges:
- Budget constraints for human spaceflight and interplanetary missions.
- Global competition from private giants like SpaceX.
- Supply chain and talent retention issues post-COVID recovery.
Nevertheless, ISRO’s culture of innovation, frugal engineering, and strong public support continue to propel it forward.
What is the Next Project of ISRO? | isro upcoming missions 2025
Exploring India’s isro upcoming missions 2025 and Future Plans | isro upcoming missions 2025
India’s space agency, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), has been making global headlines for its groundbreaking missions and innovative approach to space exploration. From the success of Chandrayaan-3, which softly landed on the Moon’s south pole, to the launch of the Aditya-L1 solar observatory, ISRO has solidified its reputation as a rising space power. But what lies ahead?
In this comprehensive article, we will explore ISRO’s next big project, along with a detailed overview of other upcoming missions (isro upcoming missions 2025) and futuristic plans that are shaping the future of Indian space research. (isro upcoming missions 2025)
ISRO
Founded in 1969, ISRO has evolved from launching basic communication satellites to conducting complex interplanetary missions. Operating under the Department of Space (DoS), ISRO’s motto — “Space technology in the service of humankind” — is reflected in both its scientific and developmental missions.
Over the years, ISRO has successfully:
- Developed indigenous launch vehicles like PSLV and GSLV
- Conducted lunar and Mars missions
- Built India’s satellite navigation system (IRNSS/NavIC)
- Entered the commercial satellite launch businessthrough Antrix and NSIL
Now, let’s look at what ISRO is planning next.
What is the Next Project of ISRO in 2025? | isro upcoming missions 2025
As of mid-2025, the next major project of ISRO is the Gaganyaan Mission — India’s first human spaceflight program. The mission is scheduled for late 2025 or early 2026, depending on the results of upcoming (isro upcoming missions 2025) test flights and astronaut training.
ISRO is also preparing for Chandrayaan-4, a sample return mission from the Moon, and Shukrayaan-1, an ambitious orbiter mission to Venus.
Key Focus Areas of ISRO’s Next Projects:
- Human spaceflight (Gaganyaan)
- Deep space exploration (Venus and Mars)
- Sample return missions (Chandrayaan-4)
- Climate and Earth observation satellites
- Expansion of satellite navigation systems
Key Upcoming ISRO Missions | isro upcoming missions 2025
Here’s a deeper look into the most anticipated ISRO projects in the coming years | isro upcoming missions 2025:
Gaganyaan Mission – India’s First Human Spaceflight
Gaganyaan is ISRO’s flagship human spaceflight program, with the goal of sending three Indian astronauts (Gagannauts) into Low Earth Orbit (LEO) for 3–7 days.
Key Details:
- Test Flight G1: Uncrewed mission completed
- Test Flight G2: Crewed flight scheduled for late 2025
- Crew Module: Designed by ISRO and HAL
- Launch Vehicle: Human-rated GSLV Mk III (LVM3)
- Training: Astronaut training is ongoing in Bengaluru and Russia
Why It Matters:
Gaganyaan is a major milestone, placing India in the elite group of countries capable of human spaceflight — joining the U.S., Russia, and China.
Chandrayaan-4 – ISRO’s Lunar Ambitions Continue
After the success of Chandrayaan-3, ISRO plans to follow up with Chandrayaan-4, a lunar sample return mission. isro upcoming missions 2025
Objectives:
- Collect lunar regolith (soil) and rock samples
- Bring samples back to Earth for scientific analysis
- Establish advanced lunar robotics and return technology
Projected Timeline:
- Launch Window: 2028–2030
- International Collaboration: Possible tie-ups with JAXA, ESA, or NASA
Shukrayaan – India’s Mission to Venus | isro upcoming missions 2025

Shukrayaan-1 is ISRO’s upcoming orbital mission to Venus, focused on understanding the planet’s thick atmosphere and geological activity. isro upcoming missions 2025
Science Goals:
- Study atmospheric chemistry and greenhouse effect
- Analyze Venus’s surface and subsurface geology
- Detect active volcanoes and lightning
Launch Details:
- Launch Vehicle: GSLV Mk II or GSLV Mk III
- Timeline: Proposed for 2028, pending government approval
Mangalyaan-2 – Second Mars Orbiter Mission
After the success of Mangalyaan-1 (Mars Orbiter Mission), ISRO is planning (isro upcoming missions 2025) MOM-2 to continue Martian exploration.
Likely Features:
- Advanced scientific payloads
- High-resolution cameras and spectrometers
- Potential lander or rover component (still under review)
Timeline:
- Post-2030, depending on funding and international partnerships
Aditya-L2 – Continuing Solar Studies
Following Aditya-L1, ISRO (isro upcoming missions 2025) is likely to propose Aditya-L2 to observe the Sun from a different Lagrange Point, offering new perspectives on solar activity.
Focus:
- Solar flares and space weather
- Long-term solar observation
- Advanced coronal and magnetosphere study
International Collaborations and Commercial Launches
ISRO (isro upcoming missions 2025) is strengthening its international partnerships, launching satellites for countries like France, Singapore, the U.K., and Brazil. Through NSIL (NewSpace India Limited), ISRO offers commercial launch services using PSLV and SSLV.
Key Partnerships:
- NASA-ISRO SAR Satellite (NISAR) – Earth science mission
- France – Ocean and climate studies
- Russia – Human spaceflight training
- UAE – Moon mission collaboration (LUPEX)
ISRO’s Role in Defense and Strategic Applications | isro upcoming missions 2025
Apart from civilian space applications, ISRO plays a role in India’s defense and security through:
- RISAT series (Radar imaging satellites)
- GSAT and GSAT-7A for secure communication
- EMISAT for electronic intelligence
- Development of space situational awareness systems
ISRO’s Vision 2047 and Beyond
As part of its long-term plan, ISRO envisions:
- Establishing a space station by 2035
- Sending Indian astronauts to the Moon by 2040
- Developing nuclear propulsion systems
- Exploring outer planets like Jupiter and Saturn
- Building self-reliant commercial space ecosystems
The Indian government has also opened the space sector to private players via IN-SPACe, enabling startups and companies to work alongside ISRO.
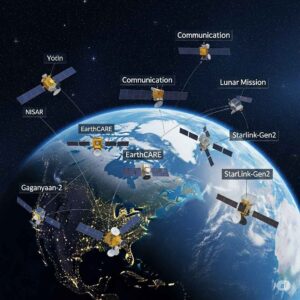
What is the Name of the Satellite in 2025? A Deep Dive into Global Satellite Launches | isro upcoming missions 2025
The year 2025 is set to be a landmark in space exploration and satellite deployment. With major space agencies like NASA, ISRO, ESA, Roscosmos, and private companies such as SpaceX, Blue Origin, and OneWeb leading ambitious missions, the skies are busier than ever. But with dozens of satellites being launched this year, a common question arises: “What is the name of the satellite in 2025?”
In this article, we’ll explore the key satellites launched or planned for launch in 2025, including their names, missions, purposes, and the countries or companies behind them. We’ll also discuss how this reflects the growing importance of satellite technology in modern society.
Introduction to Satellite Missions in 2025 | isro upcoming missions 2025%
As of 2025, humanity is relying more than ever on satellites for communication, navigation, earth observation, climate monitoring, and even defense. Several types of satellites are being launched in 2025, including:
- Communication satellites
- Earth observation satellites
- Navigation satellites
- Scientific and research satellites
- Defense satellites
- Space-based internet constellations
Let’s now explore the names of prominent satellites launched or scheduled for launch in 2025.
1. ISRO’s Satellite Launches in 2025 | isro upcoming missions 2025
a. Chandrayaan-4 (Planned)
- Type: Lunar mission with a possible sample return
- Agency: ISRO (India)
- Objective: Following the success of Chandrayaan-3, ISRO is preparing Chandrayaan-4 to further study the Moon’s south pole and potentially bring lunar soil samples back to Earth.
- Launch Window: Late 2025
b. Aditya-L2
- Type: Solar observation
- Objective: The second Aditya mission focused on studying solar wind and space weather from the Lagrange Point 2.
- Status: Planned for 2025
c. INSAT-4DS
- Type: Communication satellite
- Purpose: Enhancing telecommunication and broadcasting services in India
- Status: Launch scheduled in 2025
2. NASA’s Satellites in 2025
a. PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem)
- Type: Earth observation
- Objective: Study ocean health, climate, and air quality
- Launch Date: Early 2025
- Special Note: PACE will provide unprecedented data on Earth’s biosphere
b. Europa Clipper
- Type: Deep space probe (satellite of Jupiter’s moon Europa)
- Launch Date: October 2024 (Arrival at Europa in 2030, still a highlight in 2025 discussions)
- Mission: Search for habitable environments under Europa’s icy crust
3. ESA (European Space Agency) Satellites in 2025
a. EarthCARE (Earth Clouds, Aerosols and Radiation Explorer)
- Objective: Better understanding of cloud-aerosol-radiation interactions
- Status: Delayed to 2025
- Partner: Joint mission with JAXA (Japan)
b. Aelous-2
- Application: Climate prediction and meteorology
- Launch: Expected in mid-2025
4. SpaceX Starlink Satellites (Ongoing in 2025) | isro upcoming missions 2025
a. Starlink Gen2 Satellites
- Type: Internet communication
- Launch Count: Over 1,000 expected in 2025
- Purpose: Expanding global satellite internet coverage, especially in rural or underserved regions
- Unique Naming: Numbered as “Starlink-XXXX”
These satellites don’t have individual “names” but are tracked with serial numbers such as Starlink-6001, Starlink-6002, etc.
5. Amazon’s Project Kuiper Satellites
a. KuiperSat-1 and KuiperSat-2
- Type: Satellite broadband
- Company: Amazon
- Purpose: Compete with Starlink by providing fast and affordable satellite-based internet
- Full Constellation Goal: 3,236 satellites by 2029; major batch expected in 2025
6. China’s Satellites in 2025
a. Gaofen-13B
- Type: High-resolution earth observation
- Objective: Used for agricultural, environmental, and resource monitoring
- Agency: CNSA (China National Space Administration)
b. Beidou-4 Satellites
- Type: Navigation and positioning
- Equivalent to: U.S. GPS, Russia’s GLONASS, and EU’s Galileo
- Status: Continuously expanding; multiple launches in 2025
7. Other Notable Satellite Launches in 2025 | isro upcoming missions 2025
a. OneWeb’s Final Launches
- Purpose: Provide global broadband services
- Number of Satellites: Finalizing 648-satellite constellation
b. Rocket Lab’s Photon Satellites
- Use: Commercial space services, scientific payloads, CubeSats
- Feature: Lower-cost small satellite deployment
Why Are So Many Satellites Being Launched in 2025?
Key Drivers:
- Increase in demand for internet access
- Climate change monitoring and research
- Global navigation services
- Military surveillance and national security
- Commercial ventures in space
How Are Satellites Named?
Satellites are named based on:
- Mission objective (e.g., EarthCARE)
- Project name (e.g., Chandrayaan, Starlink)
- Serial numbers (e.g., Starlink-6010, Gaofen-13B)
There’s no single satellite called “the satellite of 2025”. Instead, there are hundreds of satellites being launched worldwide, each with a specific name and purpose.
Early Life and Education
Born on May 14, 1964, in Melakattuvilai, Kanyakumari district, Tamil Nadu, Dr. Narayanan’s journey into the realm of space science began with a diploma in mechanical engineering from Government Polytechnic College, Nagercoil.His academic pursuits culminated with an M.Tech in Cryogenic Engineering and a Ph.D. in Aerospace Engineering from the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Kharagpur .en.wikipedia.orgindiatoday.in+1en.wikipedia.org+1
Professional Trajectory at ISRO | isro upcoming missions 2025
Dr. Narayanan joined ISRO in 1984, marking the beginning of a prolific career dedicated to advancing India’s space capabilities. Notably, he served as the Director of the Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC) from January 23, 2018, to January 14, 2025 .en.wikipedia.org+10reuters.com+10indiatoday.in+10indianexpress.com+4indiatoday.in+4government.economictimes.indiatimes.com+4indiatoday.in+5en.wikipedia.org+5government.economictimes.indiatimes.com+5
He played a pivotal role in the development of the Cryogenic Upper Stage (CUS) for the GSLV Mk-II, ensuring the operational success of India’s heaviest launch vehicle, LVM3 .indiatoday.in
Contributions to India’s Space Missions | isro upcoming missions 2025
Dr. Narayanan’s contributions extend to several landmark missions:outlookindia.com+14indiatoday.in+14indiatoday.in+14
- Chandrayaan-2 and Chandrayaan-3: His work was crucial in the propulsion systems that powered these lunar missions. Chandrayaan-3 notably made India the first country to land near the Moon’s South Pole .indiatoday.in+1indiatoday.in+1
- Gaganyaan Programme: As Chairman of the National Level Human Rated Certification Board (HRCB), he played a significant role in India’s ambitious human spaceflight mission .business-standard.com+2government.economictimes.indiatimes.com+2indianexpress.com+2
- Aditya-L1 Mission: His leadership contributed to India’s first solar mission aimed at studying the Sun’s outer layers .indiatoday.in
Vision for ISRO’s Future | isro upcoming missions 2025
Under Dr. Narayanan’s leadership, ISRO is poised to undertake several ambitious projects:ddnews.gov.in+15indiatoday.in+15entrepreneur.com+15
- Gaganyaan Human Spaceflight Mission: Aiming to send Indian astronauts into space, with uncrewed test missions scheduled for later in 2025 and the first human mission set for early 2027 .reuters.com+5timesofindia.indiatimes.com+5indiatoday.in+5
- Venus Orbiter Mission: Exploring Venus to understand its atmosphere and geological features.
- Next-Generation Launch Vehicles: Developing advanced launch systems to enhance payload capacity and mission versatility.
- Indian Space Station: Establishing a space station ahead of India’s centenary of independence, with plans to launch by 2035 .timesofindia.indiatimes.com+1reuters.com+1
- Mars and Lunar Missions: Planning future explorations like the Mars mission and Chandrayaan-4 and 5 .timesofindia.indiatimes.com+1en.wikipedia.org+1
Recognition and Awards
Dr. Narayanan’s exemplary work has earned him numerous accolades:indiatoday.in+3indiatoday.in+3indiatoday.in+3
- APJ Abdul Kalam Award: Recognizing his contributions to India’s space program.
- Laurels for Team Achievement for Chandrayaan-3: Awarded by the International Academy of Astronautics for the successful lunar mission .indiatoday.in+2indiatoday.in+2indiatoday.in+2
Who is the Father of Indian Space Program? | isro upcoming missions 2025

When discussing the origins and evolution of India’s achievements in space, one name stands tall above the rest: Dr. Vikram Sarabhai
But to truly understand why Vikram Sarabhai earned this iconic title, we must journey through his life, his contributions, and the legacy he left behind — one that continues to inspire generations of scientists and space enthusiasts.
Early Life and Education of Vikram Sarabhai
The Sarabhais were known for their industrial success and philanthropy, and they were active participants in India’s freedom movement.
Vikram’s early interest in science was nurtured by this environment. He pursued higher education at the University of Cambridge, where he studied natural sciences.Post-war, he went back to Cambridge and earned a doctorate with his thesis titled “Cosmic Ray Investigations in Tropical Latitudes”, which laid the foundation for his future (isro upcoming missions 2025) work in space science.
The Vision Behind India’s Space Program
The 1960s were a pivotal era for scientific progress globally. While the U.S. and the USSR were competing in the space race, India was still a young nation grappling with poverty. He famously said:
This philosophy defined the Indian space program from the very beginning — using space for development, not dominance.
Founding of ISRO | isro upcoming missions 2025
One of Dr. Sarabhai’s greatest legacies is the establishment of ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation). In 1962, he was instrumental in setting up the Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR), under the Department of Atomic Energy. This body later evolved into ISRO in 1969, with Dr. Sarabhai as its first chairman.
Under his leadership, ISRO started its journey with a humble beginning:
- In 1963, India launched its first sounding rocket from Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station (TERLS) in Kerala.
- Equipment was carried in bullock carts.
- Yet the dreams were as vast as the sky itself.
Key Contributions of Vikram Sarabhai to Indian Science
1. Space Research and Satellite Development
Sarabhai laid the groundwork for what would eventually become India’s satellite program. His efforts led to the conceptualization of India’s first satellite, Aryabhata, which was launched in 1975, four years after his death.
2. Institution Building
- ISRO – Indian Space Research Organisation
- PRL – Physical Research Laboratory, Ahmedabad
- IIM Ahmedabad – Indian Institute of Management (co-founded with Ravi J. Matthai)
- Darpana Academy for Performing Arts – to promote cultural development
His ability to attract and motivate young scientists and engineers laid the foundation for the talent pool ISRO continues to benefit from today.
3. International Collaboration
Sarabhai understood the importance of global partnerships. He established collaborations with NASA and other international bodies. The Satellite Instructional Television Experiment (SITE) with NASA in 1975 was one of the first large-scale demonstrations of using space for education in rural India.
Legacy of Vikram Sarabhai
His successors, notably Dr. Satish Dhawan and later Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam, carried his legacy forward.
Today, India is a global space power, with achievements such as:
- Chandrayaan-1 and Chandrayaan-2 lunar missions
- Mangalyaan (Mars Orbiter Mission)
- Gaganyaan human spaceflight program (isro upcoming missions 2025)
- A growing satellite launch market serving many countries
All of this traces back to the seeds sown by Dr. Vikram Sarabhai.
In honor of his contribution:
- His birth centenary in 2019 was celebrated with national events and tributes.
Why is Vikram Sarabhai Called the Father of Indian Space Program?
Vikram Sarabhai earned this title not just for founding ISRO, but for crafting a vision that connected space science with societal development. He was among the few global scientists who saw technology not as a privilege of the elite, but as a tool to uplift the masses.
His rare combination of scientific brilliance, administrative acumen, and humanist thinking allowed him to set India’s space program on a unique path — one that the world respects today.
Who is the Father of Indian Space Program?

His visionary leadership, scientific brilliance, and unwavering dedication laid the foundation of what is now one of the world’s most respected space agencies—ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation). isro upcoming missions 2025
In this article, we delve deep into the life, achievements, and legacy of Vikram Sarabhai, exploring why he is celebrated as the Father of India’s space journey.
1. Introduction to Vikram Sarabhai
Vikram Ambalal Sarabhai was an Indian physicist, industrialist, and innovator, best known for establishing India’s space program. He was born on 12 August 1919 in Ahmedabad, Gujarat. Through his pioneering work, Sarabhai transformed India’s position in the field of science and technology. His foresight about the importance of space technology in a developing country like India changed the course of the nation’s scientific history.
2. Early Life and Education
Born into a wealthy and influential Jain family, Vikram Sarabhai was raised in an environment that encouraged learning and intellectual freedom. He pursued his early education in Ahmedabad and later moved to the United Kingdom for higher studies.
- PhD from Cambridge: After returning to India during World War II, he conducted research under Nobel laureate Sir C.V. Raman and later went back to Cambridge to complete his PhD in cosmic rays in 1947.
His academic training in physics, combined with a deep interest in nation-building, positioned him as a leader capable of merging science with societal development.
3. Scientific Vision and Founding of ISRO | isro upcoming missions 2025
The Birth of ISRO
His famous quote captures the essence of his vision:
4. Major Contributions to India’s Space Program
1. Setting up India’s First Satellite Project
- Establishing Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station (TERLS)
In 1963, Sarabhai supervised the first rocket launch from Thumba in Kerala. The first sounding rocket, Nike-Apache, was launched with American collaboration. This project was one of the largest sociological experiments ever conducted and demonstrated how satellite technology could revolutionize education in rural India.
4. Creating Institutions for Space and Science
- Physical Research Laboratory (PRL), Ahmedabad – India’s first research institute for space sciences.
- Indian Institute of Management (IIM), Ahmedabad – Alongside Kasturbhai Lalbhai.
5. Collaboration with International Space Agencies
Dr. Sarabhai was a firm believer in international cooperation in science. He successfully established collaborations with:
- NASA (USA)
- CNES (France)
- Soviet Space Agency
These collaborations helped India gain technical know-how, launch vehicles, and satellites during the early years.
6. Legacy and Honors
Vikram Sarabhai passed away suddenly on 30 December 1971, at the age of 52, but his legacy lives on through every successful Indian space mission.
Awards and Recognitions:
- Padma Bhushan (1966)
- Padma Vibhushan (posthumously in 1972)
Tributes in His Name:
- Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC) in Thiruvananthapuram
- Vikram lander on Chandrayaan-2 and Chandrayaan-3 missions
- Sarabhai Institute of Science and Technology
7. Impact on Modern-Day ISRO | isro upcoming missions 2025
Every major milestone achieved by ISRO—whether it is the Mars Orbiter Mission (Mangalyaan), Chandrayaan-2, or Aditya-L1 solar mission—is a realization of Sarabhai’s early vision.
He laid the groundwork for self-reliant satellite development, launch vehicle systems, and using space technology for education, communication, and meteorology.
8. Vikram Sarabhai vs. Other Indian Scientists
- Dr. Kalam: Known as the “Missile Man of India”, contributed to India’s missile and satellite launch capabilities.
- Satish Dhawan: Succeeded Sarabhai and operationalized many of his plans.
- U.R. Rao: Developed India’s satellite capabilities.
However, Sarabhai’s pioneering role in conceptualizing, organizing, and launching India’s space ambitions right from scratch remains unmatched.
9. Inspirational Quotes by Vikram Sarabhai
“There are who question the relevance of space activities in a developing nation. To us, there is no ambiguity of purpose.”
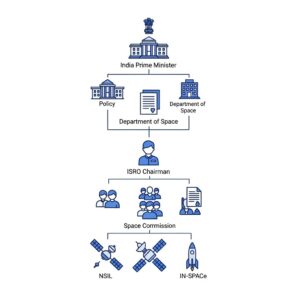
Who Controls ISRO? Understanding the Structure, Authority, and Governance of India’s Space Agency | isro upcoming missions 2025
Known for its cost-effective missions and innovative technology, ISRO has gained international recognition for achievements like the Chandrayaan lunar missions, the Mars Orbiter Mission (Mangalyaan), and its commitment to scientific advancement. But behind every successful mission is an organizational structure, a framework of control, and a network of governance. This raises an important question: Who controls ISRO?
To understand this fully, one must explore ISRO’s origins, its administrative hierarchy, its connection to the Indian government, and the strategic influence of national and international stakeholders.
The Origin and Purpose of ISRO
ISRO was established in 1969 with the vision of harnessing space technology for national development. This direct line to the highest executive office in the country gives ISRO strategic importance beyond just scientific exploration.
Who Administers ISRO? | isro upcoming missions 2025
1. Department of Space (DoS)
Created in 1972, the DoS is part of the Government of India and functions directly under the Prime Minister’s Office (PMO).
This dual role is critical as it ensures a direct link between the agency and top-level policy decisions.
2. ISRO Chairman | isro upcoming missions 2025
The Chairman of ISRO is the principal executive and scientific leader of the organization. The individual in this role is appointed by the Appointments Committee of the Cabinet (ACC), which is headed by the Prime Minister. The Chairman is responsible for strategic planning, mission oversight, budgeting, and coordination with domestic and international partners.
As of 2025, S. Somanath is the Chairman of ISRO. His leadership is pivotal in steering major projects like Gaganyaan (India’s human spaceflight program), Chandrayaan-3, and Aditya-L1 (a solar observation mission).
The Prime Minister of India serves as the Minister-in-Charge of the Department of Space. This means that ISRO, unlike many other government agencies, does not fall under a conventional ministry like the Ministry of Science and Technology or the Ministry of Defence. This structure gives ISRO a strategic edge and high-level policy backing. It allows for quicker decision-making, especially in areas of international collaboration, budget approvals, and mission authorization.
1. Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS)
For missions that have strategic or national security implications, the Cabinet Committee on Security—which includes the Prime Minister, Home Minister, Defence Minister, Finance Minister, and External Affairs Minister—plays a role in decision-making. This committee provides guidance and clearance for projects such as military satellites and strategic launches.
Other Bodies Involved in ISRO’s Governance | isro upcoming missions 2025
While the primary control of ISRO lies with the DoS and PMO, several other institutions play supporting roles in governance, research, and funding.
1. Space Commission
The Space Commission of India advises the government on space policy and oversees long-term planning for ISRO. It is a high-level advisory body comprising scientists, bureaucrats, and defense experts.
2. NITI Aayog
India’s policy think tank, NITI Aayog, occasionally collaborates with ISRO for policy formulation, particularly in areas where space-based data is required for planning and development.
3. Parliamentary Oversight
ISRO’s budget, policy changes, and performance are also subject to Parliamentary review. Questions are often raised in Parliament during budget sessions, and reports on space missions are submitted for review.
Budgetary Control and Financial Oversight
ISRO’s annual budget is proposed by the Department of Space and approved by the Ministry of Finance and Parliament.
Despite its limited budget compared to global giants like NASA or ESA, ISRO has consistently demonstrated high returns on investment through its efficient execution of complex missions.
International Collaboration and Influence
While ISRO is an autonomous entity within India’s governmental framework, its decisions and projects are often influenced by international space laws, bilateral agreements, and collaborative programs.
In these collaborations, mission planning, data sharing, and satellite launches are often governed by Memoranda of Understanding (MoUs) and inter-governmental agreements, ensuring that ISRO’s actions are aligned with international norms and India’s diplomatic interests.
Privatization and Commercial Arms: NSIL and IN-SPACe
In recent years, the Indian government has introduced reforms to open up the space sector to private players. This has added new dimensions to ISRO’s control and operational structure.
1. NewSpace India Limited (NSIL)
NSIL is a government-owned company under the Department of Space that acts as ISRO’s commercial arm. It handles the commercialization of satellite launches, transponder leasing, and technology transfer.
2. IN-SPACe
The Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center (IN-SPACe) is a regulatory body established to facilitate private sector participation in space missions. IN-SPACe ensures fair access to ISRO’s facilities, technology, and resources for non-governmental entities.
Though independent in function, both NSIL and IN-SPACe are under the overall supervision of the Department of Space and, by extension, the Government of India.
What Happened in 1965 in ISRO? A Detailed Look at a Pivotal Year in Indian Space History | isro upcoming missions 2025

While the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is globally recognized today for its cutting-edge space missions, its early years were marked by significant groundwork and foundational developments. The year 1965, although not as frequently highlighted as other landmark years, played a crucial role in shaping the direction of India’s space program.
In this article, we explore what happened in 1965 in ISRO, examining the institutional, scientific, and organizational advancements that occurred during this formative phase.
Introduction: ISRO’s Early Years | isro upcoming missions 2025
To understand the importance of 1965, it is vital to place ISRO in the context of its early evolution. ISRO, formally established in 1969, had its roots in the Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR)
During the early 1960s, INCOSPAR operated under the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) and focused on atmospheric research using sounding rockets. It was during this time that the groundwork for future (isro upcoming missions 2025) satellite and launch vehicle development was laid. By 1965, India’s scientific community had begun to solidify a clear roadmap for future space capabilities.
The Status of India’s Space Program in 1965
1. Transition from INCOSPAR to a Larger Vision
Although ISRO had not yet been officially formed, 1965 was a pivotal year in preparing for its establishment. INCOSPAR was actively expanding its research facilities and human resource base. Discussions and policy developments around creating a formal, independent space agency were gaining momentum. The idea was to transform India’s space initiatives from basic research into a strategic national program with satellite and launch vehicle development as key objectives.
One of the major achievements of the early 1960s was the establishment of the Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station (TERLS) near Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala. TERLS was inaugurated in 1963 with the successful launch of a Nike-Apache sounding rocket. By 1965, TERLS had become operationally mature and was hosting numerous sounding rocket launches for atmospheric studies.
In 1965, TERLS was not just a national facility—it had started to gain international attention. Collaborations with agencies like NASA and other international partners were taking shape, with sounding rockets being launched for joint experiments in upper atmospheric research.
3. Expansion of Research and Training
Another key development in 1965 was the expansion of training and research initiatives. Indian scientists and engineers were being sent abroad for training in advanced space technologies. Similarly, collaborations with foreign space agencies provided valuable technical know-how and infrastructure assistance.
This year marked an increase in recruitment of scientific talent, which would later form the backbone of ISRO’s workforce. Research institutions such as the Physical Research Laboratory (PRL), founded by Dr. Sarabhai, played an important role in supporting space science efforts in this period.
Scientific Developments and Technological Progress in 1965
Sounding Rocket Program | isro upcoming missions 2025
India’s sounding rocket program was in full swing by 1965. These rockets were crucial for collecting data on the Earth’s upper atmosphere, including temperature, pressure, wind patterns, and ionospheric studies.
In 1965, multiple launches of small payload rockets from TERLS were conducted. Each successful launch provided valuable scientific data and operational experience that laid the groundwork for future satellite and launch vehicle missions. (isro upcoming missions 2025)
International Collaboration
One of the defining aspects of 1965 was India’s growing collaboration with international space agencies, especially NASA. Through these partnerships, India gained access to rocket technology, telemetry systems, and data analysis techniques.
NASA assisted India in the use of sounding rockets and provided support for technical training. These collaborations were crucial in enabling India to build a foundation for an indigenous space capability.
Institutional Milestones | isro upcoming missions 2025
While ISRO as an entity did not exist in 1965, key decisions were being made within INCOSPAR and the government to shape its future. Some of the institutional developments included:
- Drafting of long-term plans for satellite development.
- Establishment of dedicated divisions within INCOSPAR for rocket engineering, atmospheric sciences, and payload development.
- Planning for future launch vehicles, which would later evolve into the Satellite Launch Vehicle (SLV) program in the 1970s.
The Role of Dr. Vikram Sarabhai in 1965 | isro upcoming missions 2025
Dr. Vikram Sarabhai continued to play a central role in guiding India’s space vision in 1965. As the chairman of INCOSPAR and director of the PRL, his leadership was critical in securing government support, fostering international cooperation, and inspiring a new generation of Indian scientists.
Sarabhai’s belief that “space research should be used for the betterment of society” was evident in the discussions and planning documents of the time. The seeds for using space technology in education, weather forecasting, and resource management were sown during this era.
Looking Ahead: The Importance of 1965 in Retrospect | isro upcoming missions 2025
When we ask what happened in 1965 in ISRO, the answer lies not in a single spectacular event, but in a series of strategic, institutional, and scientific developments. These advancements did not make headlines at the time, but they were instrumental in laying the foundation for the remarkable successes of ISRO in the decades that followed.
The groundwork laid in 1965 enabled:
- The formal establishment of ISRO in 1969.
- The eventual creation of advanced missions like Chandrayaan, Mangalyaan, and Gaganyaan.
–


